Need for Plasticizers and Its Types
Need for Plasticizers and Its Types
Plasticizers are additives that increase the plasticity or fluidity of a material. Coating formulations based on physically drying binders such as nitrocellulose, require external plasticizers for optimal film formation.
They are used to control the film formation process of coatings based on physically drying film-forming materials. Proper film formation is essential in order to meet demands on specific coating properties such as:
- Dry film appearance
- Substrate adhesion
- Elasticity
- Hardness
The molecules in polymeric film-forming materials, such as nitrocellulose (NC), typically show low chain mobility, explained by strong molecular interaction (explained by van der Waals forces) of the polymer chains.
Let's study the role of plasticizers based on their chemistry alongwith the types of plasticizers used in coating formulations...
Role of Plasticizers
Role of Plasticizers
The role of the plasticizer is to reduce or entirely prevent the formation of such bridging bonds. In case of synthetic polymers, this can be achieved by incorporating elasticizing segments or monomers which sterically hinder molecular interaction.
This chemical modification process is known as "inner plasticization". For natural products or hard polymers of poor processing, the option is the external use
of plasticizers in the coating formulations.
Plasticizers interact physically with the polymer binder molecule, without a chemical reaction and form a homogeneous system. The interaction is based on the specific structure of the plasticizer, typically containing polar and non-polar moieties, and results in lowering the glass temperature (Tg).
In order to ensure high efficiency, the plasticizer should be able to
penetrating in the resin at film-forming conditions. Commonly used plasticizers
in coatings are:
- Phthalate esters such as DOP
- ATBC (citrates)
- DOA
- DINA (adipates)
- DINCH (dicarboxylate) and more.
Use of Plasticizers in Coatings
Use of Plasticizers in Coatings
 Plasticizers are used in coating formulations (for instance in NC lacquers) for
the following purposes:
Plasticizers are used in coating formulations (for instance in NC lacquers) for
the following purposes:
- To enable proper film formation
- To improve film appearance & gloss
- To improve mechanical film properties, such as adhesive strength, flexibility
& elongation
- To increase resistance to light, heat, sudden temperature changes (cold-check test)
Plasticizers may be solvents or non-solvents to the binder. For
example, NC is soluble in plasticizers such as di-butyl phthalate (DBP), di-iso-octyl phthalate (DIOP), di-octyl phthalate (DOP)
& tricresyl phosphate. However, NC is insoluble in plasticizers like main stearates and oleates.
Main external plasticizers are low molecular weight materials, demonstrating fast interaction with the polymer chain. However, in specific cases also, polymers are used as plasticizing material. For instance, NC lacquers may be modified using synthetic resins such as alkyd resins to control flexibility and reduce brittleness. These lacquers are known as "nitro-combination lacquers" and are physical/ chemical drying systems. Other group of resins used for this purpose are polyurethane resins as well as acrylic resins and ketone resins.
A large variety of plasticizers are produced, but less than 100 compositions are in commercial use.
The class of chemicals called "phthalates" are the most commonly used plasticizers. They are colorless
& odorless liquids, manufactured in large quantities.
In Europe, more than 90% of the total volume phthalates are produced & used to plasticize PVC (polyvinyl chloride) to make flexible PVC products. Only a fraction of the production volume is used in coating formulations.
The most common phthalates are:
- Di-isononyl phthalate (DINP)
- Di-isodecyl phthalate (DIDP)
- Di-2-ethyl hexyl phthalate (DEHP), and
- Di-n-octyl phthalate (DOP)
One of the main concern for these chemicals is potential migration of the phthalate plasticizer
from the coated or printed external surface (for instance packaging material) through the film, onto the foodstuff contained within.
Obviously, for packaging inks & especially food packaging, phthalates will not be the plasticizer of choice anymore, hence other alternatives of plasticizers are being selected instead.
Phthalate-based Plasticizers
Phthalate-based Plasticizers
Di-n-octyl phthalate (DOP)
 DOP or DnOP is light-colored, low volatility & odorless liquid. It was
the most commonly used all-purpose plasticizer, although mainly used for polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resins. It is insoluble in water
& has a low viscosity of 56 mPa.s at 25°C. DOP features:
DOP or DnOP is light-colored, low volatility & odorless liquid. It was
the most commonly used all-purpose plasticizer, although mainly used for polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resins. It is insoluble in water
& has a low viscosity of 56 mPa.s at 25°C. DOP features:
- Good stability to heat and ultraviolet light
- Broad range of compatibility, and
- Excellent resistance to hydrolysis
Di-iso-octyl phthalate (DIOP)
DIOP is like DOP, an all-purpose plasticizer for polyvinyl chloride, polyvinyl acetate, rubbers, cellulose plastics, and polyurethane.
Di-iso-nonyl phthalate (DINP) & Di-iso-decyl phthalate (DIDP)
DINP & DIDP are low-cost plasticizers that have been widely used in coating formulations. These plasticizers have been preferred, enabling the formulation of coatings
like highly-durable repair coatings for train, tram, metro and cranes rendering good elasticity and hardness properties.
Other Plasticizers
Other Plasticizers
The interest for alternative materials has increased strongly and resulted in the introduction of various products.
Some alternative plasticizers as proposed for coatings are ATBC, SAIB, DOA and EPO.
Although main properties of phthalate-based plasticizers can be met,
the other alternative products tend to be more sensitive to migration as compared to DOP or DIOP.
Acetyl Tri-Butyl Citrate (ATBC)
ATBC is considered as a safe, low toxicity, alternative plasticizer demonstrating improved biodegradability and biochemical properties, as compared to phthalates.
ATBC is widely used now for NC coatings as well as NC food packaging inks & packaging of medical products. ATBC tends to be more sensitive to migration as compared to DOP, although still low as compared to other
plasticizers. One of the applications of ATBC is in lacquers for toys.
Dioctyl Adipate (DOA)
DOA is a diester of adipic acid and two equivalents of n-octanol. Its chemical formula is C22H42O4. DEHA is sometimes incorrectly called dioctyl adipate; it is di 2-ethylhexyl adipate, so the branched version of DOA.
Chemical structure of Dioctyl adipate
DOA features:
- Low temperature flexibility,
- Good electrical properties,
- Good resistance to weathering, and
- Good stability to heat
DOA is used to produce clear films for food packaging applications. In addition, it is compatible with nitrocellulose, ethyl cellulose, most synthetic rubbers and high-butyryl cellulose acetate butyrate.
According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), it is "not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans" (Group 3), suggesting inadequate evidence of human carcinogenicity.
NC Ink Formulation with DOA Plasticizer
|
Ink Formulation
|
%
|
|
NC varnish*
|
10.75
|
|
Pigment concentrate**
|
43.0
|
|
Plasticizer
|
8.6
|
|
IMS 99%
|
25.1
|
|
Ethyl acetate
|
12.55
|
|
*NC Varnish
|
%
|
|
Nitrocellulose 3/5DLX
|
40
|
|
IMS 99%
|
40
|
|
Ethyl acetate
|
20
|
|
**White NC Ink pigment concentrate
|
%
|
|
Nitrocellulose DLX 5-8
|
10
|
|
Ethanol
|
20
|
|
Ethyl acetate
|
7
|
|
Di-octyl adipate
|
3
|
|
Titanium dioxide
|
60
|
Di(2-ethylhexyl) Adipate (DEHA)
DEHA is the diester of adipic acid and 2-ethylhexanol, same chemical formula as DOA: C22H42O4. DEHA is a plasticizer that gives flexibility at low temperatures as well as good heat stability. It is used to produce packaging films for food applications and is compatible with nitrocellulose, ethyl cellulose and most rubber compounds.
DEHA is used mainly in food packaging inks. However, compared to ATBC it tends to demonstrate stronger tendency to migration.
Di-isononyl Adipate (DINA)
DINA is used as a low-temperature resistant and light-resistant plasticizer for PVC, its copolymers and rubbers. It is permitted in the field of food additive, food contact material. It is used as a carrier solvent for polyurethane system.
Di-isononyl-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylate (DINCH)
DINCH was introduced in 2002 as a plasticizer for PVC applications like medical appliances, toys or food applications.
Chemical Structure of DINCH
Alkylsulphonic Acid Ester of Phenol (ASE)
ASE is a multi-purpose plasticizer with a good gelling behavior and an exceptional saponification resistance. It is compatible with many types of polymers including polyurethanes.
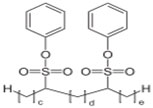 Chemical Structure of ASE
Chemical Structure of ASE
Plasticizers for Paints & Coatings
View a wide range of plasticizer grades available in the market today, analyze technical data of each product, get technical assistance or request samples.